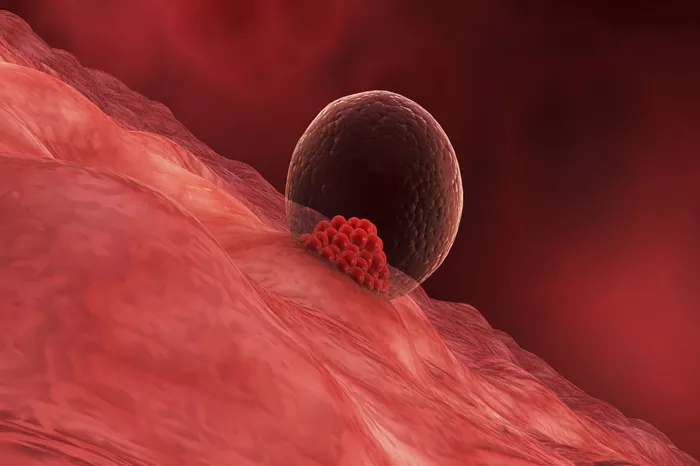
Implantation is a critical event in early pregnancy. It marks the moment when a fertilized egg, or blastocyst, attaches to the lining of the uterus. This process sets the stage for pregnancy to continue and develop. For many women trying to conceive, recognizing implantation symptoms can be both exciting and anxiety-inducing. This article will explore the timing of implantation symptoms, their nature, and what they indicate about early pregnancy.
The Journey to Implantation
Fertilization to Implantation
After ovulation, an egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube. If sperm are present, fertilization typically occurs within 24 hours. The fertilized egg, now called a zygote, begins to divide and form a cluster of cells. This cluster is known as a blastocyst by the time it reaches the uterus, usually around 5-6 days after fertilization.
The Implantation Window
Implantation typically occurs between 6 to 10 days after ovulation. This period is known as the “implantation window.” The exact timing can vary based on several factors, including the length of the woman’s menstrual cycle and the health of the blastocyst. During this window, the blastocyst attaches itself to the endometrial lining of the uterus, initiating the release of hormones essential for maintaining pregnancy.
Early Signs of Implantation
Many women wonder when they might start noticing signs of implantation. While every woman’s body is different, implantation symptoms generally start around 6 to 12 days after ovulation. Here’s a detailed look at the symptoms that may signal implantation:
Implantation Bleeding
Timing: Implantation bleeding usually occurs around 6 to 12 days after ovulation.
Nature: It is typically light spotting, much lighter than a regular
menstrual period. The bleeding can range in color from pink to brown.
Duration: This bleeding usually lasts for a few hours to a couple of days.
Cause: The bleeding happens as the blastocyst burrows into the uterine lining, disrupting small blood vessels.
Cramping
Timing: Implantation cramping can occur simultaneously with implantation bleeding, usually around 6 to 12 days post-ovulation.
Nature: These cramps are usually mild and less intense than menstrual cramps. They are often described as a pulling or tugging sensation.
Duration: The cramps may last from a few hours to a couple of days.
Cause: The cramping results from the uterine lining adjusting to the implanted blastocyst.
Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Changes
Timing: A woman tracking her BBT may notice a slight dip in temperature around 7 to 10 days after ovulation.
Nature: This dip, known as an implantation dip, is followed by a rise in temperature.
Duration: The dip is usually brief, lasting only one day.
Cause: Hormonal changes related to implantation can cause this temporary fluctuation.
Breast Changes
Timing: Breast tenderness or changes can begin as early as a few days after implantation.
Nature: Women may experience swelling, tenderness, or a tingling sensation in their breasts. The areolas may also darken.
Duration: These symptoms can persist throughout early pregnancy.
Cause: Hormonal changes, particularly the increase in progesterone, cause these breast changes.
Fatigue
Timing: Fatigue can start around the time of implantation and continue throughout early pregnancy.
Nature: Women may feel unusually tired or find they need more sleep than usual.
Duration: Fatigue often continues into the first trimester.
Cause: The body’s increased production of progesterone can lead to feelings of fatigue and tiredness.
Nausea and Food Aversions
Timing: While more commonly associated with later stages of pregnancy, some women may experience nausea or food aversions shortly after implantation.
Nature: This symptom is often mild at first but can become more pronounced as pregnancy progresses.
Duration: These symptoms can persist into the first trimester.
Cause: Hormonal changes, particularly rising levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), contribute to nausea and food aversions.
The Role of Hormones in Implantation Symptoms
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
hCG is a hormone produced by the cells of the placenta shortly after implantation. It is crucial for maintaining the corpus luteum, which in turn supports the production of progesterone during early pregnancy. Rising levels of hCG are responsible for many early pregnancy symptoms.
Progesterone
Progesterone plays a vital role in preparing the endometrial lining for implantation and maintaining early pregnancy. It causes many of the physical changes associated with early pregnancy, such as breast tenderness, fatigue, and nausea.
Estrogen
Estrogen levels also rise after implantation. This hormone works alongside progesterone to support the developing pregnancy and can contribute to symptoms like breast changes and nausea.
Differentiating Implantation Symptoms from PMS
Timing Differences
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms usually begin a week or two before a woman’s period. In contrast, implantation symptoms occur about 6 to 12 days after ovulation, which is typically a few days to a week before the expected period.
Symptom Differences
While some symptoms of PMS and implantation overlap (such as cramping and breast tenderness), implantation symptoms tend to be milder and shorter in duration. Additionally, implantation bleeding is distinct from the heavier menstrual flow typical of a period.
Hormonal Causes
Both PMS and implantation symptoms are hormonally driven. However, PMS is primarily influenced by cyclical changes in estrogen and progesterone, while implantation symptoms result from the specific hormonal changes associated with early pregnancy.
Confirming Implantation
Home Pregnancy Tests
Home pregnancy tests detect hCG in urine. For the most accurate results, it’s best to wait until at least the first day of a missed period, although some sensitive tests may detect pregnancy a few days earlier. Testing too soon can result in a false negative due to low hCG levels.
Blood Tests
A blood test at a doctor’s office can detect lower levels of hCG and confirm pregnancy earlier than a home test. These tests can provide more detailed information about hCG levels and help track the progression of early pregnancy.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound can provide visual confirmation of pregnancy and implantation. However, it is usually not performed until several weeks into the pregnancy, once the embryo and gestational sac are visible.
When to See a Doctor
Unusual Bleeding
If bleeding is heavy, persistent, or accompanied by severe pain, it’s important to see a doctor. This could indicate a potential complication such as an ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage.
Severe Pain
Mild cramping is normal during implantation, but severe or persistent pain should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to rule out complications.
Confirmation of Pregnancy
Regardless of symptoms, it’s essential to confirm pregnancy with a healthcare provider. They can provide guidance on next steps and ensure both the mother’s and baby’s health are monitored appropriately.
Factors Influencing Implantation
Uterine Health
The health of the uterine lining is crucial for successful implantation. Conditions such as endometriosis, fibroids, or polyps can affect implantation.
Hormonal Balance
Proper hormonal balance is essential for implantation. Disorders like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid dysfunction can interfere with this process.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors such as stress, diet, and exercise can influence hormonal balance and overall reproductive health, potentially affecting implantation.
Age
A woman’s age can impact the likelihood of successful implantation. Fertility typically declines with age, and older women may face more challenges in achieving and maintaining pregnancy.
Supporting Implantation and Early Pregnancy
Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall reproductive health. Nutrients like folic acid, iron, and calcium are particularly important during early pregnancy.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can affect hormonal balance. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and regular exercise can help manage stress levels.
Adequate Sleep
Getting enough sleep is essential for maintaining hormonal balance and overall health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Avoiding Harmful Substances
Avoiding substances such as alcohol, tobacco, and excessive caffeine can support a healthy pregnancy. These substances can interfere with hormonal balance and affect fetal development.
Conclusion
Implantation is a complex and critical step in the journey to pregnancy. Understanding the timing and nature of implantation symptoms can help women recognize early signs of pregnancy and differentiate them from PMS. While implantation symptoms typically start around 6 to 12 days after ovulation, individual experiences may vary. Paying attention to one’s body and confirming pregnancy with a healthcare provider are essential steps in ensuring a healthy and successful pregnancy journey.
By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and being aware of the signs and symptoms of implantation, women can feel more confident and informed as they navigate the early stages of pregnancy.