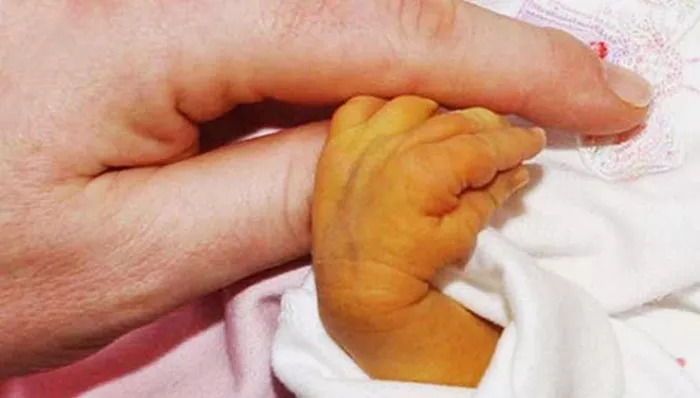
Jaundice is a condition characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes due to elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells. When the liver cannot process bilirubin efficiently or when there is an excess production of bilirubin, jaundice occurs. Common causes include liver disease, hepatitis, blockage of bile ducts, and certain medications. Symptoms of jaundice include yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark urine, fatigue, and abdominal pain.
Medical Consultation
The first and most crucial step in managing jaundice is to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional will perform a physical examination, review medical history, and may order blood tests or imaging studies to determine the underlying cause of jaundice. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and promote recovery.
Dietary Recommendations
Diet plays a significant role in managing jaundice, as certain foods can support liver function and help reduce bilirubin levels. It is essential to follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Foods that are beneficial for liver health include:
1. Leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and collard greens
2. Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits
3. Nuts and seeds, especially those high in omega-3 fatty acids like walnuts and flaxseeds
3. Lean proteins such as fish, chicken, and tofu
5. Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread
Avoid foods high in saturated fats, sugar, and processed ingredients, as they can strain the liver. Limiting alcohol intake is also crucial, as alcohol can worsen liver damage and hinder recovery.
Hydration
Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and can help the liver function more efficiently. Drinking an adequate amount of water helps flush toxins from the body, including excess bilirubin. Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day, and consider consuming hydrating foods such as watermelon, cucumbers, and soups.
Avoiding Harmful Substances
In addition to alcohol, certain medications and substances can be harmful to individuals with jaundice. Always consult with a healthcare provider before taking any medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Some medications, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can be taxing on the liver and should be used cautiously or avoided altogether.
Newborn Care
For parents of newborns with jaundice, proper care is essential to ensure their well-being. Follow these tips for newborn care:
1. Ensure regular feeding, whether breastfeeding or formula feeding, as frequent feeding promotes bowel movements, aiding in bilirubin elimination.
2. Monitor diaper output to ensure the baby is producing an adequate number of wet and soiled diapers.
3. Keep the baby’s skin protected from excessive sunlight, as sun exposure can worsen jaundice in newborns. If sunlight exposure is necessary, do so in moderation and under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Warning Signs
While most cases of jaundice resolve without complications, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. Seek medical help if you experience:
1. Severe abdominal pain
2. Persistent vomiting
4. Extreme fatigue or weakness
5. Changes in mental status, such as confusion or disorientation
5. Dark urine or pale stools
These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition or complications of jaundice that require prompt evaluation and treatment.
Home Care Tips
Supporting recovery at home is crucial for individuals with jaundice. Follow these home care tips:
1. Get plenty of rest to allow the body to heal and recover.
2. Avoid strenuous physical activities or heavy lifting that can strain the body.
3. Follow medical advice regarding medication use and dietary restrictions.
4. Maintain a clean and hygienic environment to prevent infections.
Follow-Up
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor the progress of jaundice and adjust treatment as needed. Follow medical recommendations regarding follow-up visits, blood tests, and imaging studies to ensure optimal care and recovery.
In conclusion, understanding what not to do in jaundice is crucial for effectively managing the condition and preventing complications. Consultation with healthcare professionals, maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, avoiding harmful substances, and following medical advice are key steps in promoting recovery and overall well-being. By following these guidelines and seeking prompt medical attention for any concerning symptoms, individuals can navigate jaundice with informed decision-making and optimal care.