Expectant parents or caregivers often seek guidance on how to prevent jaundice in newborns during pregnancy, aiming to understand and mitigate the risk factors associated with this common condition. Jaundice, characterized by the yellowing of the skin and eyes due to elevated bilirubin levels, affects a significant number of newborns worldwide. However, with proactive measures and proper medical guidance, it is largely preventable and manageable. This article aims to provide comprehensive information and practical advice on preventing jaundice in newborns during pregnancy.
Understanding Newborn Jaundice
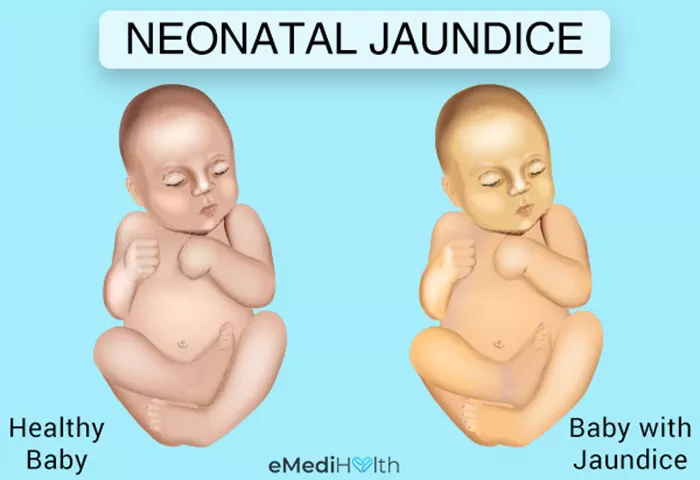
Newborn jaundice occurs when there is an accumulation of bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells, in the baby’s blood. Bilirubin is typically processed by the liver and eliminated through feces. However, in newborns, the liver may take some time to mature and efficiently process bilirubin, leading to its buildup in the bloodstream¹.
Symptoms of jaundice include yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, which usually become noticeable within a few days after birth. While jaundice is generally harmless, in some cases, particularly when bilirubin levels are very high, it may indicate underlying health issues and require medical attention¹.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of newborn jaundice. These include blood type incompatibilities between the mother and baby, preterm birth, and genetic enzyme deficiencies¹.
1. Blood Type Incompatibilities: Incompatibility between the mother’s and baby’s blood types, particularly regarding the Rh factor, can lead to jaundice. When a mother is Rh-negative and the baby is Rh-positive, the mother’s immune system may produce antibodies that attack the baby’s red blood cells, leading to an increase in bilirubin levels¹.
2. Preterm Birth: Premature babies are at a higher risk of jaundice due to their underdeveloped liver function, which may not be able to efficiently process bilirubin.
3. Genetic Enzyme Deficiencies: Certain genetic conditions, such as glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, can affect the breakdown of red blood cells, leading to increased bilirubin levels in newborns.
Preventative Measures During Pregnancy
Taking proactive steps during pregnancy can significantly reduce the risk of newborn jaundice.
1. Regular Prenatal Check-ups: Attending regular prenatal check-ups is crucial for monitoring the mother’s and baby’s health throughout pregnancy. Healthcare providers can identify any potential risk factors for jaundice and provide appropriate guidance and interventions³.
2. Blood Type and Rh Factor Testing: Blood tests to determine the mother’s blood type and Rh factor are essential for identifying potential incompatibilities with the baby’s blood. If the mother is Rh-negative, additional testing and interventions may be necessary to prevent Rh incompatibility-related jaundice¹.
3. Genetic Counseling: Families with a history of severe jaundice or genetic disorders associated with increased bilirubin levels should consider genetic counseling. This can help assess the risk of jaundice in the newborn and provide guidance on preventive measures and treatment options³.
4. Managing Maternal Health Conditions: Effectively managing maternal health conditions, such as diabetes or thyroid disorders, can help reduce the risk of complications during pregnancy, including newborn jaundice³.
Nutrition and Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition during pregnancy can contribute to the overall well-being of both the mother and baby, reducing the risk of jaundice.
1. Well-Balanced Diet: A diet rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins and minerals, supports fetal development and helps ensure optimal liver function in both the mother and baby.
2. Avoiding Substances: Pregnant women should avoid substances known to increase the risk of jaundice in newborns, such as alcohol and certain medications. It’s essential to consult healthcare providers before taking any medications during pregnancy⁵.
Postnatal Care
After the baby is born, continued vigilance and proper care are essential for preventing and managing jaundice.
1. Early and Frequent Breastfeeding: Breastfeeding provides essential nutrients and fluids to newborns and helps promote the passage of meconium, the baby’s first stool, which contains bilirubin. Early and frequent breastfeeding can help prevent and reduce jaundice³.
2. Proper Hydration: Ensuring that the newborn is adequately hydrated is crucial for preventing dehydration, which can exacerbate jaundice. Mothers should monitor their baby’s feeding and urine output and seek medical advice if there are concerns about hydration³.
3. Monitoring Blood Type Incompatibility: Babies at risk of jaundice due to blood type incompatibility should be closely monitored for signs of jaundice. Healthcare providers may recommend additional testing or interventions, such as phototherapy, if bilirubin levels become elevated³.
Treatment Options
In cases where preventive measures are not sufficient, various treatment options are available to manage newborn jaundice.
1. Phototherapy: Phototherapy involves exposing the baby’s skin to special lights that help break down bilirubin into a form that can be more easily eliminated from the body³.
2. Exchange Transfusion: In severe cases of jaundice, particularly those caused by blood type incompatibility, exchange transfusion may be necessary. This procedure involves replacing the baby’s blood with compatible donor blood to reduce bilirubin levels³.
Conclusion
While newborn jaundice is a common occurrence, understanding its risk factors and taking proactive measures during pregnancy can help prevent and manage the condition effectively. Regular prenatal care, genetic counseling, proper nutrition, and postnatal monitoring are essential components of jaundice prevention. It’s crucial for expectant parents to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance throughout pregnancy and after childbirth. With proper care and timely interventions, most cases of newborn jaundice can be successfully treated, ensuring the health and well-being of both mother and baby.