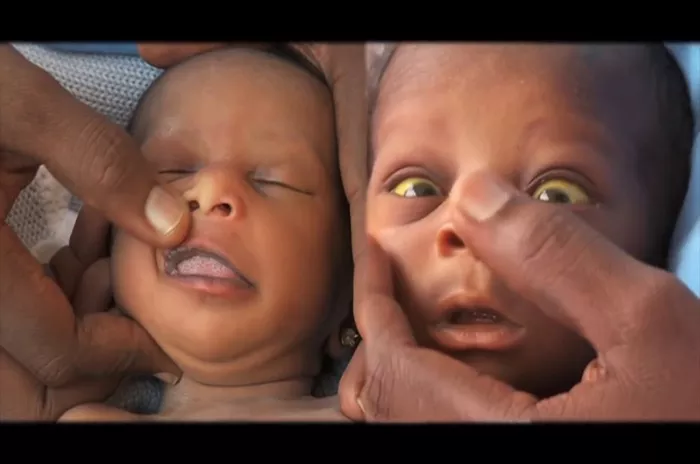
Newborn jaundice is a common condition that affects many infants shortly after birth. It is characterized by a yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes, caused by an elevated level of bilirubin in the baby’s blood. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment produced during the normal breakdown of red blood cells. In newborns, this pigment can accumulate faster than the liver can process and eliminate it, leading to jaundice.
There are several types of jaundice in newborns, including physiological jaundice, which is considered normal and usually resolves on its own, and pathological jaundice, which can be more serious and may require medical intervention. Understanding the basics of jaundice and recognizing the symptoms early is crucial for ensuring the health and well-being of your newborn.
Symptoms to Monitor
Recognizing the signs of jaundice in a newborn is the first step in addressing the condition. Common symptoms include:
1.Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes: This is the most noticeable sign. The yellow tint usually starts on the face and chest and can spread to other parts of the body.
2.Lethargy: A jaundiced baby may be more sleepy or difficult to wake up.
3.Poor Feeding: Babies with jaundice might have trouble breastfeeding or taking a bottle.
4.Dark Urine: Urine may appear darker than usual.
5.Pale Stools: Stools might be lighter in color, which can indicate higher bilirubin levels.
Importance of Medical Evaluation
While mild jaundice is often harmless and resolves on its own, it is vital to seek medical evaluation to determine the severity and appropriate treatment. A healthcare provider can conduct a physical examination and measure bilirubin levels through a blood test or a skin test using a device called a bilirubinometer. Severe jaundice can lead to serious complications such as kernicterus, a type of brain damage caused by very high bilirubin levels. Therefore, early detection and monitoring by a healthcare professional are essential.
Home Remedies
For mild cases of jaundice, certain home remedies can help lower bilirubin levels and support the baby’s recovery. However, these should always be used in conjunction with medical advice.
1.Frequent Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding is one of the most effective ways to reduce jaundice in newborns. Regular feeding helps to increase bowel movements, which aids in the excretion of bilirubin.
2.Sunlight Exposure
Exposure to natural sunlight can help reduce bilirubin levels, as sunlight helps to break down bilirubin in the skin.
3.Baby Massage
Gentle massage can stimulate circulation and potentially aid in the breakdown of bilirubin. Use light, circular motions on the baby’s abdomen and back. Ensure your hands are clean and warm.
Dietary Considerations for Mothers
The diet of a breastfeeding mother can influence the effectiveness of breastfeeding and the baby’s overall health. A well-balanced diet ensures that the mother is producing sufficient and nutrient-rich milk.
1.Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to maintain adequate milk supply.
2.Balanced Diet: Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, proteins, and healthy fats.
3.Avoid Certain Foods: Limit the intake of caffeine and avoid alcohol, as these can affect milk supply and quality.
Safe Home Care Practices
Caring for a jaundiced baby at home involves ensuring the baby is well-hydrated, monitored, and kept comfortable.
1.Hydration: Keep the baby hydrated through regular breastfeeding or formula feeding.
2.Monitoring: Keep a close watch on the baby’s symptoms. Track feeding times, diaper changes, and any changes in behavior or appearance.
3.Comfort: Ensure the baby is dressed in comfortable, loose-fitting clothes. Maintain a calm and soothing environment to reduce stress for both the baby and the caregivers.
Recognizing Complications
While many cases of jaundice are mild, it is crucial to recognize signs that indicate a need for immediate medical attention. These include:
1.Increased Yellowing: If the yellowing spreads or becomes more intense.
2.High Fever: Any fever in a newborn should be taken seriously.
3.Extreme Lethargy: Difficulty waking the baby or significant changes in activity levels.
4.Poor Feeding: Refusal to eat or difficulties in feeding persistently.
5.Unusual Crying: High-pitched or inconsolable crying.
Conclusion
Newborn jaundice is a common and typically manageable condition. By understanding the symptoms, ensuring a medical evaluation, and utilizing safe home remedies like frequent breastfeeding, safe sunlight exposure, and gentle baby massage, parents can effectively support their baby’s health. However, it is imperative to follow professional medical advice and seek immediate attention if complications arise. With the right care and monitoring, most babies recover fully without long-term effects.