Cervical mucus plays a crucial role in the female reproductive system. It changes throughout the menstrual cycle in response to hormonal fluctuations, serving as a vital indicator of fertility. One of the most significant stages in the menstrual cycle is implantation, which marks the beginning of pregnancy. This article delves into the nature of cervical mucus after implantation, examining its characteristics, significance, and how it reflects the intricate processes occurring within the body.
The Role of Cervical Mucus
Cervical mucus is produced by glands in the cervix. Its primary functions include:
1. Facilitating sperm transport.
2. Providing a protective barrier against pathogens.
3. Helping maintain a healthy vaginal environment.
The consistency and volume of cervical mucus vary significantly throughout the menstrual cycle, influenced mainly by estrogen and progesterone levels.
The Menstrual Cycle and Cervical Mucus
Understanding the changes in cervical mucus throughout the menstrual cycle is essential for grasping its significance after implantation. Here’s a brief overview:
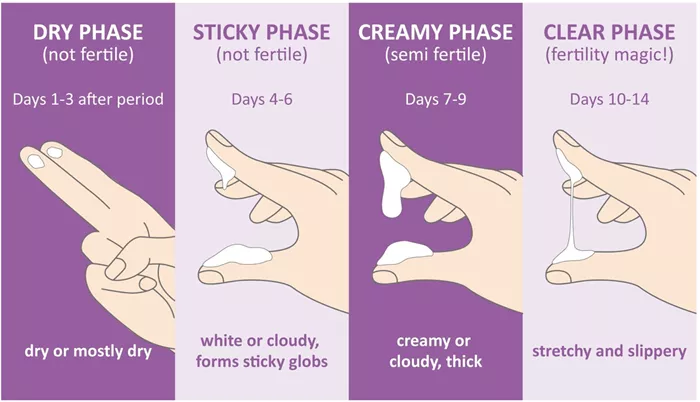
1. Menstruation Phase: During menstruation, cervical mucus is minimal and mixed with blood.
2. Follicular Phase: As estrogen levels rise, cervical mucus becomes more abundant, clear, and stretchy, resembling egg whites. This facilitates sperm movement.
3. Ovulation: At ovulation, cervical mucus is at its peak in terms of quantity and fertility. It is slippery and stretchable, aiding sperm in reaching the egg.
4. Luteal Phase: After ovulation, progesterone dominates, causing cervical mucus to become thick and sticky, forming a barrier to protect the potential pregnancy.
5. Implantation: A Critical Phase
Implantation occurs approximately 6-12 days after ovulation. During this process, the fertilized egg (blastocyst) embeds itself into the uterine lining. This marks the beginning of pregnancy and triggers a cascade of hormonal changes, particularly an increase in human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), estrogen, and progesterone.
Changes in Cervical Mucus After Implantation
After implantation, cervical mucus undergoes notable changes. These changes are primarily due to the hormonal shifts that support pregnancy. Here’s what to expect:
1. Increased Progesterone Levels:
Progesterone is crucial for maintaining pregnancy. It thickens cervical mucus to form a mucus plug, protecting the uterus from infections.
2. Consistency and Appearance:
Thicker and Stickier: Cervical mucus after implantation becomes thicker and stickier. This change is protective, sealing the cervix to create a barrier against pathogens.
White or Creamy: The color often changes to a white or creamy hue. This is a significant change from the clear, egg-white consistency observed during ovulation.
Increased Volume: Some women notice an increase in cervical mucus volume after implantation, although this is not universal.
3.Other Characteristics:
1. Opaque and Dense: Post-implantation cervical mucus is usually more opaque and denser compared to the fertile mucus of the ovulatory phase.
2. Mucus Plug Formation: As pregnancy progresses, the mucus continues to thicken, eventually forming a mucus plug. This plug remains in place throughout pregnancy, ensuring the uterus remains sealed off from external contaminants.
Cervical Mucus and Early Pregnancy Symptoms
The changes in cervical mucus after implantation are often accompanied by other early pregnancy symptoms. These symptoms, along with cervical mucus changes, can provide valuable clues about conception. Common early pregnancy symptoms include:
1. Missed Period: A missed menstrual period is one of the most obvious signs of pregnancy.
2. Breast Changes: Tender, swollen, or sensitive breasts are common early indicators.
3 .Fatigue: Increased progesterone levels can cause fatigue.
4. Nausea: Often referred to as morning sickness, nausea can occur at any time of the day.
5. Frequent Urination: Hormonal changes increase blood flow to the kidneys, causing more frequent urination.
Monitoring Cervical Mucus for Pregnancy Detection
Many women track their cervical mucus to understand their menstrual cycle better and to identify potential pregnancy early. Here’s how to monitor cervical mucus effectively:
1. Daily Observation: Check cervical mucus daily, preferably at the same time each day. This helps in noting subtle changes.
2. Consistency Check: Use clean fingers to assess the consistency of cervical mucus. Record whether it is sticky, creamy, or stretchy.
3. Color and Volume: Observe any changes in color and volume. Note if the mucus becomes whiter, creamier, or increases in volume.
The Science Behind Cervical Mucus Changes
The changes in cervical mucus after implantation are driven by hormonal shifts. Understanding the underlying science provides clarity on why these changes occur.
1. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG): After implantation, the developing placenta produces hCG. This hormone supports the corpus luteum, which in turn maintains progesterone production.
2. Progesterone: As progesterone levels rise, cervical mucus thickens. This hormone is crucial for sustaining the uterine lining and preventing menstruation.
3. Estrogen: Although progesterone dominates, estrogen also plays a role in maintaining pregnancy. It helps regulate the balance of mucus production and other physiological processes.
Cervical Mucus and Fertility Awareness
Fertility awareness involves tracking menstrual cycle symptoms, including cervical mucus, to determine fertile windows and detect pregnancy. Here’s how cervical mucus fits into fertility awareness methods:
1. Ovulation Prediction: Clear, stretchy, and egg-white cervical mucus indicates ovulation. Recognizing this type of mucus helps in identifying the most fertile days.
2. Luteal Phase Tracking: Post-ovulation, cervical mucus becomes thicker and less fertile. Observing this change helps confirm the end of the fertile window.
3. Early Pregnancy Detection: Changes in cervical mucus consistency and appearance after the expected implantation time can signal early pregnancy.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While changes in cervical mucus can be a helpful indicator of implantation and early pregnancy, it’s essential to seek medical advice in certain situations:
1. Abnormal Discharge: If cervical mucus has an unusual color (green or yellow), odor, or causes irritation, it may indicate an infection.
2. Absence of Expected Changes: If expected changes in cervical mucus do not occur, or if there are other concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider.
3. Confirming Pregnancy: While cervical mucus changes can suggest pregnancy, a home pregnancy test and a healthcare provider’s confirmation are necessary for accurate diagnosis.
Cervical Mucus and Pregnancy Health
Monitoring cervical mucus isn’t just for detecting pregnancy; it also provides insights into overall reproductive health during pregnancy.
1. Infection Prevention: The mucus plug formed post-implantation plays a critical role in preventing infections by sealing the cervix.
2. Signs of Complications: Unusual changes in cervical mucus during pregnancy, such as a sudden increase in volume or changes in color, can indicate complications like infections or preterm labor.
3. Regular Check-Ups: Regular prenatal visits help ensure that any abnormalities in cervical mucus or other symptoms are promptly addressed.
Common Misconceptions About Cervical Mucus After Implantation
There are several misconceptions about cervical mucus and its changes after implantation. Clarifying these can help women better understand their bodies:
1. Cervical Mucus as a Definitive Pregnancy Indicator: While changes in cervical mucus can suggest pregnancy, they are not definitive. Other symptoms and medical tests are necessary for confirmation.
2. Uniform Changes for All Women: Not all women experience the same changes in cervical mucus after implantation. Variations are normal and depend on individual hormonal responses.
3. Immediate Changes Post-Implantation: Changes in cervical mucus may not be immediate. It can take several days after implantation for noticeable changes to occur.
Supporting Reproductive Health
Understanding cervical mucus changes and their significance after implantation is part of broader reproductive health awareness. Here are some tips for supporting reproductive health:
1. Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep support hormonal balance and reproductive health.
2. Hydration: Staying hydrated helps maintain healthy cervical mucus production.
3. Avoiding Harmful Substances: Limiting alcohol, caffeine, and avoiding smoking can positively impact reproductive health.
4. Regular Health Check-Ups: Regular visits to a healthcare provider ensure that any issues are identified and addressed early.
Conclusion
Cervical mucus after implantation undergoes significant changes due to hormonal shifts that support pregnancy. These changes, including thicker and stickier consistency, white or creamy color, and increased volume, provide valuable insights into early pregnancy. While monitoring cervical mucus is a useful tool for fertility awareness and early pregnancy detection, it should be complemented by medical tests and consultations for accurate diagnosis and comprehensive reproductive health care. Understanding and observing these changes empower women to take an active role in their reproductive health, enhancing awareness and preparedness throughout their reproductive journey.